Activated sludge process
 Activated sludge is a process dealing with the treatment of sewage and industrial wastewaters and developed around 1912-1914.[1] Atmospheric air or pure oxygen is introduced to a mixture of primary treated or screened sewage (or industrial wastewater) combined with organisms to develop a biological floc which reduces the organic content of the sewage
Activated sludge is a process dealing with the treatment of sewage and industrial wastewaters and developed around 1912-1914.[1] Atmospheric air or pure oxygen is introduced to a mixture of primary treated or screened sewage (or industrial wastewater) combined with organisms to develop a biological floc which reduces the organic content of the sewage
MBBR – Moving Bed bioreactor
 Wastewater treatment plants of a medium or small scale require a simple equipment composition and easy maintenance. The Moving-Bed type bioreactor has largely simplified the washing mechanism by washing filtering media parallelly to the reactor processing.
Wastewater treatment plants of a medium or small scale require a simple equipment composition and easy maintenance. The Moving-Bed type bioreactor has largely simplified the washing mechanism by washing filtering media parallelly to the reactor processing.
SBR -Sequence batch reactor
 Sequencing batch reactors (SBR) or sequential batch reactors are industrial processing tanks for the treatment of wastewater. SBR reactors treat waste water such as sewage or output from anaerobic digesters or mechanical biological treatment facilities in batches. Oxygen is bubbled through the waste water to reduce biochemical oxygen demand (BOD) and chemical oxygen demand (COD) to make suitable for discharge into sewers or for use on land.
Sequencing batch reactors (SBR) or sequential batch reactors are industrial processing tanks for the treatment of wastewater. SBR reactors treat waste water such as sewage or output from anaerobic digesters or mechanical biological treatment facilities in batches. Oxygen is bubbled through the waste water to reduce biochemical oxygen demand (BOD) and chemical oxygen demand (COD) to make suitable for discharge into sewers or for use on land.
MBR -membrane bio reactor
 Membrane bioreactor (MBR) is the combination of a membrane process like microfiltration or ultrafiltration with a suspended growth bioreactor, and is now widely used for municipal and industrial wastewater treatment with plant sizes up to 80,000 population equivalent (i.e. 48 MLD) [1].
Membrane bioreactor (MBR) is the combination of a membrane process like microfiltration or ultrafiltration with a suspended growth bioreactor, and is now widely used for municipal and industrial wastewater treatment with plant sizes up to 80,000 population equivalent (i.e. 48 MLD) [1].
SAF -submerged aerobic filter
 This system consists of partially or totally submerged biological support material and improves the efficiency of biological filtration. In submerged or flooded aerobic filter, effluent flows down through a bed of small natural or plastic media. Air is injected into the base of bed. Hence waste water can be applied at a much higher rate than conventional filters. There is a second filtration stage below the injection point where removal of solids generated in the upper aerobic mixed zone occurs. Solids, on accumulation in the lower filter stage, reduce a critical stage in clearing by backwashing. Wash water is returned to the treatment plant for settlement.
This system consists of partially or totally submerged biological support material and improves the efficiency of biological filtration. In submerged or flooded aerobic filter, effluent flows down through a bed of small natural or plastic media. Air is injected into the base of bed. Hence waste water can be applied at a much higher rate than conventional filters. There is a second filtration stage below the injection point where removal of solids generated in the upper aerobic mixed zone occurs. Solids, on accumulation in the lower filter stage, reduce a critical stage in clearing by backwashing. Wash water is returned to the treatment plant for settlement.
UASB – Up flow anaerobic sludge blanket reactor
 The Upflow Anaerobic Sludge Blanket Reactor (UASB) is a single tank process. Wastewater enters the reactor from the bottom, and flows upward. A suspended sludge blanket filters and treats the wastewater as the wastewater flows through it.
The Upflow Anaerobic Sludge Blanket Reactor (UASB) is a single tank process. Wastewater enters the reactor from the bottom, and flows upward. A suspended sludge blanket filters and treats the wastewater as the wastewater flows through it.
Lagoon Aeration Systems
 An aerated lagoon or aerated basin is a holding and/or treatment pond provided with artificial aeration to promote the biological oxidation of wastewaters.[1][2][3] There are many other biological processes for treatment of wastewaters, for example activated sludge, trickling filters, rotating biological contactors and biofilters. They all have in common the use of oxygen (or air) and microbial action to biotreat the pollutants in wastewaters.
An aerated lagoon or aerated basin is a holding and/or treatment pond provided with artificial aeration to promote the biological oxidation of wastewaters.[1][2][3] There are many other biological processes for treatment of wastewaters, for example activated sludge, trickling filters, rotating biological contactors and biofilters. They all have in common the use of oxygen (or air) and microbial action to biotreat the pollutants in wastewaters.
Oxidation Ditches
 Treatment of wastewater using an oxidation ditch is relatively similar to wastewater treatment in a packaged plant. But the oxidation ditch replaces the aeration basin and provides better sludge treatment
Treatment of wastewater using an oxidation ditch is relatively similar to wastewater treatment in a packaged plant. But the oxidation ditch replaces the aeration basin and provides better sludge treatment
Grey water treatment systems
 Greywater is wastewater generated from domestic activities such as laundry, dishwashing, and bathing which can be recycled on-site for uses such as landscape irrigation and constructed wetlands. Greywater differs from water from the toilets which is designated sewage or blackwater to indicate it contains human waste.
Greywater is wastewater generated from domestic activities such as laundry, dishwashing, and bathing which can be recycled on-site for uses such as landscape irrigation and constructed wetlands. Greywater differs from water from the toilets which is designated sewage or blackwater to indicate it contains human waste.
Package Treatment Plants
The selection of a packaged wastewater treatment plant offers the user a pre-engineered and pre-fabricated method of treating wastewater with an aerobic process. The final effluent can be released safely into the environment such as receiving streams, rivers, etc. Treated non-potable water is also being used as a new source of water to promote agricultural and aquaculture production, industrial uses, water sustainability, and reclamation uses such as irrigation, wash down, and / or artificial recharge
Enzyme Enhancement systems
Fine Bubble Diffusers
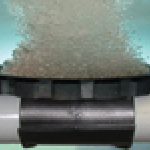 Fine bubble diffusers are a pollution control technology. They produce a plethora of very small air bubbles which rise slowly from the floor of a wastewater treatment plant or sewage treatment plant aeration tank and provide substantial and efficient mass transfer of oxygen to the water. The oxygen, combined with the food source, sewage, allows the bacteria to produce enzymes which help break down the waste so that it can settle in the secondary clarifiers or be filtered by membranes.
Fine bubble diffusers are a pollution control technology. They produce a plethora of very small air bubbles which rise slowly from the floor of a wastewater treatment plant or sewage treatment plant aeration tank and provide substantial and efficient mass transfer of oxygen to the water. The oxygen, combined with the food source, sewage, allows the bacteria to produce enzymes which help break down the waste so that it can settle in the secondary clarifiers or be filtered by membranes.
Coarse Bubble Diffusers
 Coarse bubble diffusers offer moderate oxygen transfer efficiency and low maintenance. EDI’s full spectrum of coarse bubble diffuser platforms offer advances in mechanical reliability, application flexibility, and ease of installation and maintenance.
Coarse bubble diffusers offer moderate oxygen transfer efficiency and low maintenance. EDI’s full spectrum of coarse bubble diffuser platforms offer advances in mechanical reliability, application flexibility, and ease of installation and maintenance.
Lagoon Aeration Systems
Coarse bubble diffusers offer moderate oxygen transfer efficiency and low maintenance. EDI’s full spectrum of coarse bubble diffuser platforms offer advances in mechanical reliability, application flexibility, and ease of installation and maintenance.
Venturi Aeration Systems
 Aeraton by Venturi is unique to Super-Treat and is a patented device.The treatment process relies principally on oxygenating the wastewater.To do this the Super-Treat system uses the Venturi method, driven by a submersible water pump which draws in air which is mixed with effluent in a frothing action.
Aeraton by Venturi is unique to Super-Treat and is a patented device.The treatment process relies principally on oxygenating the wastewater.To do this the Super-Treat system uses the Venturi method, driven by a submersible water pump which draws in air which is mixed with effluent in a frothing action.
Air Blowers

Anti Foam Dosing systems
Antifoam is dosed upstream of the deaerator to minimise the effect of foaming in the deaerator.
Hopper Bottom Clarifiers
 We provide blanket desludging systems for flat bottom and hopper bottom clarifiers.
We provide blanket desludging systems for flat bottom and hopper bottom clarifiers.
Components of a typical assembly include:
Sludge cone, Gravilectric load cell , Automatic desludging valve, Distribution trident, Desludging hose.
Lamella Clarifiers
 A lamellaR clarifier is a water treatment process that features a rack of inclined metal plates, which cause flocculated material to precipitate from water that flows across the plates.
A lamellaR clarifier is a water treatment process that features a rack of inclined metal plates, which cause flocculated material to precipitate from water that flows across the plates.
Inclined plate settlers or lamellaR clarifiers are primarily used in the water and wastewater treatment industries to separate solids from liquids in effluent streams. The clarifier is the third step in what is usually a four step process for water and wastewater treatment. In wastewater treatment the four main steps are collection and homogenization of effluent, pH adjustment, clarification, and sludge dewatering.
Fbiolo
 Dissolved air flotation (DAF) is a water treatment process that clarifies wastewaters (or other waters) by the removal of suspended matter such as oil or solids. The removal is achieved by dissolving air in the water or wastewater under pressure and then releasing the air at atmospheric pressure in a flotation tank or basin. The released air forms tiny bubbles which adhere to the suspended matter causing the suspended matter to float to the surface of the water where it may then be removed by a skimming device.
Dissolved air flotation (DAF) is a water treatment process that clarifies wastewaters (or other waters) by the removal of suspended matter such as oil or solids. The removal is achieved by dissolving air in the water or wastewater under pressure and then releasing the air at atmospheric pressure in a flotation tank or basin. The released air forms tiny bubbles which adhere to the suspended matter causing the suspended matter to float to the surface of the water where it may then be removed by a skimming device.
Dissolved air flotation is very widely used in treating the industrial wastewater effluents from oil refineries, petrochemical and chemical plants, natural gas processing plants, paper mills, general water treatment and similar industrial facilities. A very similar process known as induced gas flotation is also used for wastewater treatment. Froth flotation is commonly used in the processing of mineral ores.
Oil Skimmers
 Oil skimmers are pieces of equipment that remove oil floating on the surface of a fluid. In general, oil skimmers work because they are made of materials to which oil is more likely to stick than the fluid it is floating on. At the same time, the fluid has very little attraction to oil skimmers.
Oil skimmers are pieces of equipment that remove oil floating on the surface of a fluid. In general, oil skimmers work because they are made of materials to which oil is more likely to stick than the fluid it is floating on. At the same time, the fluid has very little attraction to oil skimmers.
Heavy Metals Removal
 A new chemical blend works so well for heavy metal removal from waste water that it seems impossible: faster reaction times, removal of 21 identified heavy metals in one pass, and reduced sludge volumes. The metals include copper (Cu), nickel (Ni), zinc (Zn, chrome (Cr), and cadmium (Cd). Complicated treatment routines with multiple chemicals are eliminated. Wastes can be mixed, with no need to separate waste streams. A bonus is the elimination of the common sulfur smell generated by other processes.
A new chemical blend works so well for heavy metal removal from waste water that it seems impossible: faster reaction times, removal of 21 identified heavy metals in one pass, and reduced sludge volumes. The metals include copper (Cu), nickel (Ni), zinc (Zn, chrome (Cr), and cadmium (Cd). Complicated treatment routines with multiple chemicals are eliminated. Wastes can be mixed, with no need to separate waste streams. A bonus is the elimination of the common sulfur smell generated by other processes.
Neutralisation systems
 The Multi-Tank Neutralization Systems include one reaction tank that is skid-mounted or supplied with a catwalk frame and are piped and wired. The systems are designed to adjust the pH either up, down or both.
The Multi-Tank Neutralization Systems include one reaction tank that is skid-mounted or supplied with a catwalk frame and are piped and wired. The systems are designed to adjust the pH either up, down or both.
BOD & COD removal systems
TSS removal systems
Biological Sludge Stabilsation
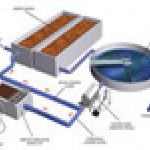 Biological stabilization techniques for sludge basically consist of slowing down or even stopping the putrid fermentation that leads to odour pollution.
Biological stabilization techniques for sludge basically consist of slowing down or even stopping the putrid fermentation that leads to odour pollution.
Sludge Drying Beds – Solar Drying
 Sludge drying beds rely on drainage and evaporation to effect moisture reduction.These beds are open; and, as such, are very susceptible to climatic conditions such as precipitation, sunshine,air temperature, relative humidity, and wind velocity. For example, sludge drying in 6 weeks in summerwould take at least 12 weeks to dry in the winter. Sludge bed drying efficiency can be improved significantlyby covering the bed with glass or plastic and by providing artificial heat. Heat could be supplied using wastebiogas as a fuel or waste heat from the base power plant.
Sludge drying beds rely on drainage and evaporation to effect moisture reduction.These beds are open; and, as such, are very susceptible to climatic conditions such as precipitation, sunshine,air temperature, relative humidity, and wind velocity. For example, sludge drying in 6 weeks in summerwould take at least 12 weeks to dry in the winter. Sludge bed drying efficiency can be improved significantlyby covering the bed with glass or plastic and by providing artificial heat. Heat could be supplied using wastebiogas as a fuel or waste heat from the base power plant.
Plate & Frame Filter Press
 Plate and frame filter presses are dewatering machines which utilize pressure (60-80 psi, typically) to remove the liquid from a liquid-solid slurry. They are particularly suited for low solids (<2% solids), or solids composed of fines (-200 mesh), however they will essentially dewater many combinations of particle size distribution and percent solid slurries. The diagram at left, shows the basic operation of a plate and frame filter press. The feed enters the press at the bottom of the plate, using a pump suitable for pumping up to 80-90 psi. Then, the feed travels the path of least resistance (up bewteen the filter plates), which has filter media inserted between the plates, and the void between the plates is filled with the slurry, as the liquid passes through the filter media, and travels up to the outlet port at the top of the plate. This liquid is referred to as the “filtrate”, and is discharged from the press. The solids remain in the void between the plates, until the plates discharge the filtered solids.
Plate and frame filter presses are dewatering machines which utilize pressure (60-80 psi, typically) to remove the liquid from a liquid-solid slurry. They are particularly suited for low solids (<2% solids), or solids composed of fines (-200 mesh), however they will essentially dewater many combinations of particle size distribution and percent solid slurries. The diagram at left, shows the basic operation of a plate and frame filter press. The feed enters the press at the bottom of the plate, using a pump suitable for pumping up to 80-90 psi. Then, the feed travels the path of least resistance (up bewteen the filter plates), which has filter media inserted between the plates, and the void between the plates is filled with the slurry, as the liquid passes through the filter media, and travels up to the outlet port at the top of the plate. This liquid is referred to as the “filtrate”, and is discharged from the press. The solids remain in the void between the plates, until the plates discharge the filtered solids.
Belt Press
The Belt Filter Press is used to dewater sludge from 1-6% solids and mineral slurries from 6-25% solids. The products processed are typically delivered to the Belt Filter Press via a positive displacement pump.
Centrifuge
Centrifuges used in water and wastewater treatment operations dewater, or remove, the liquid from the residual solids produced in the treatment process. Containing less water, the dewatered material is easier to handle and costs less to transport.
Sludge Composting
Simply stated, composting is the biological decomposition of the organic constituents of wastes under controlled conditions. The term “decomposition” is used instead of “stabilization”, because when applied to a practical usage, the process is rarely carried on to the point at which the waste is completely stabilized. the term “biological” distinguishes composting from other types of decomposition, such as chemical or physical. Organic is applicable because, with few exceptions, only the organic portion of wastes is subject to biological breakdown. A very important term in the definition of composting is “controlled”. It is the application of control that distinguishes composting from the natural rotting, putrefaction, or other decomposition, that takes place in an open dump, a sanitary landfill, in a manure heap, or in an open field.
TSE Recycle
Vehicle Wash Water Recycle
 We offers line of vehicle wash water recycle equipment to recycle wash water and provide high quality water for vehicle washing. Suitable for car wash, truck wash, bus wash, and train wash systems.
We offers line of vehicle wash water recycle equipment to recycle wash water and provide high quality water for vehicle washing. Suitable for car wash, truck wash, bus wash, and train wash systems.
Laundry Wastewater Recycle
 AquaRecycle™ has revolutionized the laundry industry by applying a proven water purification process to the laundry environment. Our filtration and treatment process provides clean, disinfected and pre-heated water to the washing machines. Our AquaSmart® technology tracks system performance, guarantees recycled water quality and provides complete automation of the system.
AquaRecycle™ has revolutionized the laundry industry by applying a proven water purification process to the laundry environment. Our filtration and treatment process provides clean, disinfected and pre-heated water to the washing machines. Our AquaSmart® technology tracks system performance, guarantees recycled water quality and provides complete automation of the system.
Cooling Water Blowdown
Activated Carbon Adsorption
offers a line of activated carbon filters for adsorption of organic compounds from contaminated water and air streams. Liquid phase filters have capacities up to 500 gpm and are available in low pressure or high pressure design. Vapor phase filters have capacities up to 20,000 cfm and are available in ‘up flow’ or ‘radial flow’ design. A variety of high activity activated carbons are available to suit your application. All equipment is designed for a low pressure drop.
Activated Carbon Dry Systems
Activated carbon is a well tried and tested adsorbent with a wide range of applications. It is produced by controlled burning of carbon rich materials such as coal, wood or nut shell. It is either steam or chemically activated to further develop its internal pore structure. Many activated carbons have enormous internal surface areas in the region of 1200m² which makes them effective adsorbents.
Chemical Liquid Scrubber Systems
Wet scrubber is a form of pollution control technology. The term describes a variety of devices that remove pollutants from a furnace flue gas or from other gas streams. In a wet scrubber, the polluted gas stream is brought into contact with the scrubbing liquid, by spraying it with the liquid, by forcing it through a pool of liquid, or by some other contact method, so as to remove the pollutants.
Biological Filters
 Biofiltration is a biological wastewater treatment technology used in municipal, steel, and chemical manufacturing facilities, solid waste processing plants, composting operations, and rendering plants. Biological systems use microorganisms that consume and destroy organic compounds as a food source.
Biofiltration is a biological wastewater treatment technology used in municipal, steel, and chemical manufacturing facilities, solid waste processing plants, composting operations, and rendering plants. Biological systems use microorganisms that consume and destroy organic compounds as a food source.
Odor Masking Chemical Compounds
Our product is a concentrated deodorant specially designed to mask odors associated with the wastewater treatment industry. When adding the concentrate to wastewater, unpleasant odors will be masked by a fragrance.
Odor Abatement Chemicals Dosing Systems
Our odor control feed and storage systems are designed to provide reliable handling and dosing of chemicals to treat odors and corrosion associated with these wastewaters. Any place or process in which wastewater is collected, conveyed or treated has the potential to generate and release nuisance odors to the surrounding area.
- Hospital Waste
- Heavy Metals
- Laboratory Waste
- Nuclear Waste
- Municipal Solid Waste
Penstocks, Manual & Motorised
 A penstock is a sluice or gate or intake structure that controls water flow, or an enclosed pipe that delivers water to hydraulic turbines and sewerage systems. It is a term that has been inherited from the technology of wooden watermills.
A penstock is a sluice or gate or intake structure that controls water flow, or an enclosed pipe that delivers water to hydraulic turbines and sewerage systems. It is a term that has been inherited from the technology of wooden watermills.
Stop Logs
 Stoplogs are a hydraulic engineering control element that are used in floodgates to adjust the water level and/or flow rate in a river, canal, or reservoir. Stoplogs are sometimes confused with flashboards, as both elements are used in bulkhead or crest gates. Stoplogs are typically long rectangular timber beams or boards that are placed on top of each other and dropped into premade slots inside a weir, gate, or channel. Other materials, including steel and composites, can be used as stoplogs as well. Stoplogs are designed to cut off or stop flow through a conduit.
Stoplogs are a hydraulic engineering control element that are used in floodgates to adjust the water level and/or flow rate in a river, canal, or reservoir. Stoplogs are sometimes confused with flashboards, as both elements are used in bulkhead or crest gates. Stoplogs are typically long rectangular timber beams or boards that are placed on top of each other and dropped into premade slots inside a weir, gate, or channel. Other materials, including steel and composites, can be used as stoplogs as well. Stoplogs are designed to cut off or stop flow through a conduit.
Manual Bar Screens
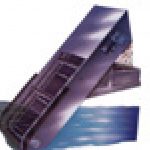 Bar screens are typically at the headworks (entrance) of a wastewater treatment plant (WWTP), bar screens are used to remove large objects such as rags, plastics bottles, bricks, solids, and toy action figures from the waste stream entering the treatment plant. Bar screens are vital to the successful operation of a plant, they reduce the damage of valves, pumps, and other appurtenances. Floatables are also removed at the entrance to a treatment plant, these are objects that “float” on the surface of the water and if aren’t removed end up in the primaries or aeration tanks. It is not uncommon to see floatables hanging over the weirs of some clarifiers. Though they don’t diminish the function of those processes, floatables are rather unsightly.
Bar screens are typically at the headworks (entrance) of a wastewater treatment plant (WWTP), bar screens are used to remove large objects such as rags, plastics bottles, bricks, solids, and toy action figures from the waste stream entering the treatment plant. Bar screens are vital to the successful operation of a plant, they reduce the damage of valves, pumps, and other appurtenances. Floatables are also removed at the entrance to a treatment plant, these are objects that “float” on the surface of the water and if aren’t removed end up in the primaries or aeration tanks. It is not uncommon to see floatables hanging over the weirs of some clarifiers. Though they don’t diminish the function of those processes, floatables are rather unsightly.
Mechanical Bar Screens
Bar screens are typically at the headworks (entrance) of a wastewater treatment plant (WWTP), bar screens are used to remove large objects such as rags, plastics bottles, bricks, solids, and toy action figures from the waste stream entering the treatment plant. Bar screens are vital to the successful operation of a plant, they reduce the damage of valves, pumps, and other appurtenances. Floatables are also removed at the entrance to a treatment plant, these are objects that “float” on the surface of the water and if aren’t removed end up in the primaries or aeration tanks. It is not uncommon to see floatables hanging over the weirs of some clarifiers. Though they don’t diminish the function of those processes, floatables are rather unsightly.
Static Fine Screens
 Fine screens are used over a wide range of applications. Applications that typically use fine screens are pre-treatment in conjunction with a coarse bar screen, primary treatment in lieu of primary clarifiers, and pre-treatment at combined sewer overflows. When clogging of trickling filters presents the potential for a problem, it is common to use fine screens upstream of the trickling filters to remove solids from the primary effluent.
Fine screens are used over a wide range of applications. Applications that typically use fine screens are pre-treatment in conjunction with a coarse bar screen, primary treatment in lieu of primary clarifiers, and pre-treatment at combined sewer overflows. When clogging of trickling filters presents the potential for a problem, it is common to use fine screens upstream of the trickling filters to remove solids from the primary effluent.
Rotary Drum Screens
 Rotary Drum Screens utilize a cylindrical drum constructed of wedge wire screen to remove solid materials from waste streams at capacities from 200 to 4,650 gal/min. (757 to 17,600 liter/min.). Effluent discharges from a head box, overflows a dam and flows onto the outside of the rotating cylinder, allowing water to pass through the wedgewire into the cylinder. A doctor blade scrapes sludge and debris collected on the outside of the cylinder, while an internal spray line dislodges particles blinding the screen.
Rotary Drum Screens utilize a cylindrical drum constructed of wedge wire screen to remove solid materials from waste streams at capacities from 200 to 4,650 gal/min. (757 to 17,600 liter/min.). Effluent discharges from a head box, overflows a dam and flows onto the outside of the rotating cylinder, allowing water to pass through the wedgewire into the cylinder. A doctor blade scrapes sludge and debris collected on the outside of the cylinder, while an internal spray line dislodges particles blinding the screen.
Filters
Ultrafiltration
Ultrafiltration (UF) is a variety of membrane filtration in which hydrostatic pressure forces a liquid against a semipermeable membrane. Suspended solids and solutes of high molecular weight are retained, while water and low molecular weight solutes pass through the membrane. This separation process is used in industry and research for purifying and concentrating macromolecular (103 – 106 Da) solutions, especially protein solutions. Ultrafiltration is not fundamentally different from microfiltration or nanofiltration, except in terms of the size of the molecules it retains. Ultrafiltration is applied in cross-flow or dead-end mode and separation in ultrafiltration undergoes concentration polarization.
